Features of the detergent additive behavior in gasolines of different group composition
Engineering Journal: Science and Innovation
# 11·2017 21
taining the maximum amount of aromatic hydrocarbons in the absence of
oxygenates. The minimum effect was obtained on the samples of the base
fuel at petrol No. 4, with a minimal content of aromatic hydrocarbons too
high content of oxygenates. He was about 1.6 % reduction in fuel con-
sumption, however, as mentioned above, when the concentration of the
additive input of more than 2000 ppm, perhaps the effect would be higher.
However, the increase of concentration of multifunctional additives leads
to an unacceptable increase in the cost of fuel.
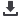
This result correlates with data on the content of a toxic component in
exhaust gases on the content of CH (Fig. 5).
Obviously, improving the speed and quality of combustion of fuel
provided by the input activator of combustion, leading to reduced fuel
consumption, contributes to a more complete combustion of the gasoline
in the cylinder which is manifested in the reduction of residual hydrocar-
bons CH. The maximum effect is achieved in the above defined concentra-
tions, input of additives, in accordance with the composition of the base
gasoline. In this case, and the relative effect size also correlates with data
obtained in the analysis of the fuel efficiency of an engine working on dif-
ferent fuel samples. Thus, the maximum reduction effect of CH is
achieved on the samples of the fuels on the basis of the base gasoline,
No. 1 (7.5 %), the minimum — fuel samples based on base gasoline No. 4
(to 3.6 %).
Fig. 5.
The dependence of the relative content of residual hydrocarbons
HC in the exhaust gases from the concentration of input additives