A.Yu. Shabanov, Yu.V. Galyshev, A.B. Zaytsev, S.V. Butorov
20
Engineering Journal: Science and Innovation
# 11·2017
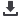
Some results of the performed tests is given below. Fig. 4 shows the
dependence of the relative change of averaged fuel specific consumption
of the engine when operating on gasoline containing the additive, the con-
centration of its input in the fuel.
Fig. 4.
The dependence of the relative change in specific fuel consump-
tion the concentration of the input multifunctional additives
In Fig. 4 the graphs show a pronounced dependence of the optimal
additive concentration at which the maximum energy-saving effect, from
the group composition of gasoline. Also it is clearly seen the dependence
of this parameter from the content in oxygenated gasoline component. So,
for gasoline samples No. 1 and No. 2 not containing in the composition of
oxygenates, the value of an optimal concentration close (about 1300 ppm),
which exceeds the stated manufacturer of the additive (1000 ppm). For
gasoline containing bound oxygen, optimum concentration is shifted in a
big way. So, for sample No. 3, the best results are obtained when the con-
centration 1600 ppm of the additive. Moreover, for gasoline No. 4 in the
studied range of concentrations the optimum was not determined, that is, it
is achieved at the concentration of the additive substantially in excess of
2000 ppm.
Also the curves in Fig. 4 show the effect of fuel composition on the
efficiency of the activator burning. The greatest effect (about 3.5 % reduc-
tion in fuel consumption relative to operation of the engine on base gaso-
line) obtained at the fuels, based on which the base gasoline No. 1, con-