Features of the detergent additive behavior in gasolines of different group composition
Engineering Journal: Science and Innovation
# 11·2017 15
As follows from the results of determination of physico-chemical
characteristics of the base gasoline and samples of No. 1–3 belong to envi-
ronmental class K5 and fully comply with the requirements of Technical
regulations of the Customs Union TR CU 013/2011. Sample No. 4 does
not meet these requirements in composition (the presence of methanol),
mass fraction of oxygen and sulfur. It is a typical representative of gas
condensate of baseline gasoline, frequently used part of the fuel compa-
nies with a low turnover of fuel. Despite the illegitimacy of the composi-
tion of this sample of gasoline, it was decided to leave it in the study to
expand the range of parameters of the group composition of the fuel. The
results of the extended analysis of hydrocarbon composition of the sam-
ples of the base fuels represented in table 2.
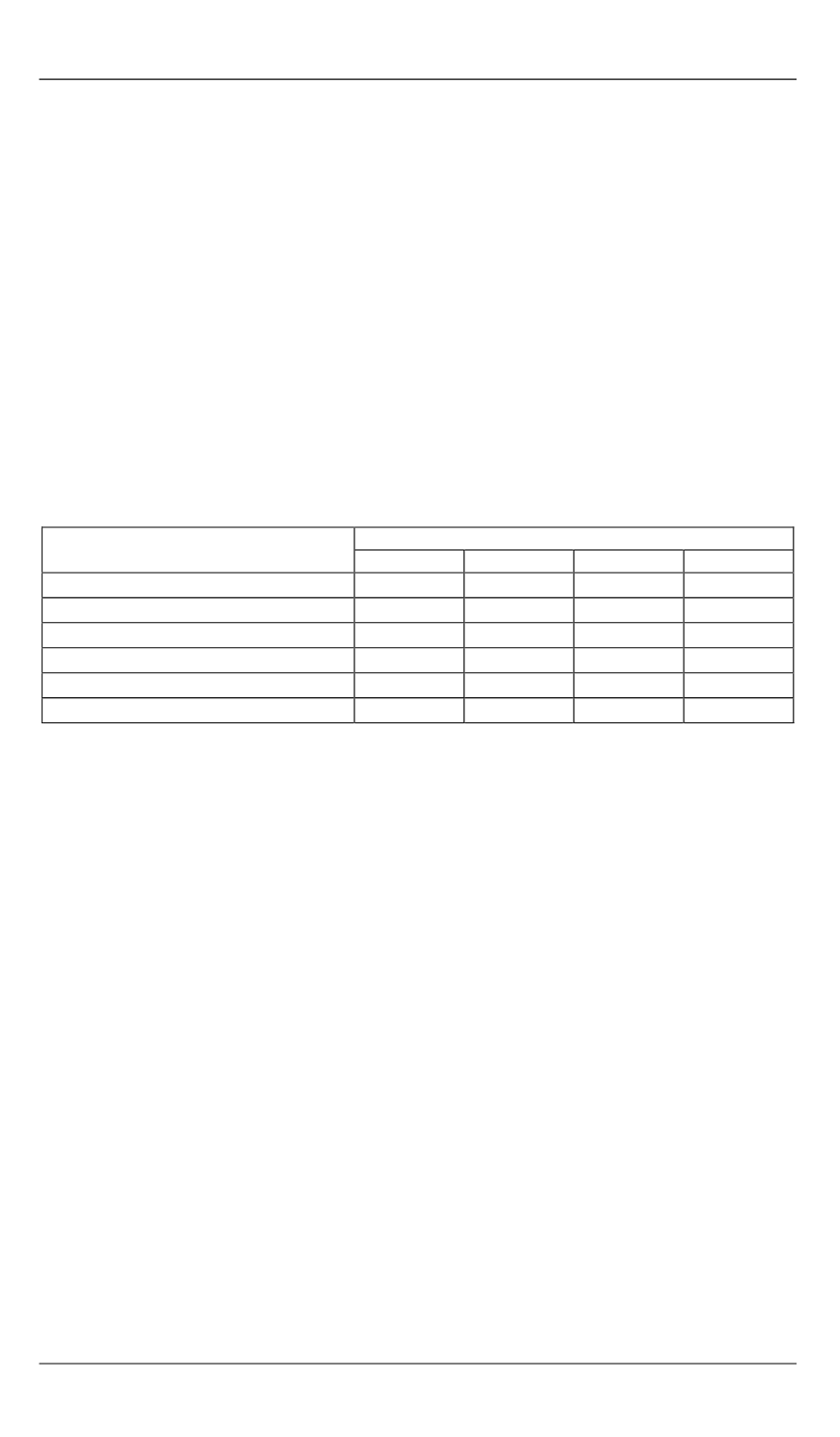
Table 2
The content of hydrocarbons of certain groups
in the studied samples of the base gasoline, % v/v
The group of hydrocarbons
A sample of gasoline
No. 1
No. 2
No. 3
No. 4
N-paraffin
11.43
12.04
12.55
18.47
Isoparaffin
47.23
48.54
40.54
31.43
Aromatic
34.87
33.04
25.88
16.34
Naphthenic
3.92
5.26
5.14
10.14
Olefin
2.55
0.42
4.18
2.08
Oxygenates
0
0.70
11.71
21.54
Tests were successively conducted for each sample of gasoline, then
for the same gasoline with multifunctional additives introduced into the
fuel at a concentration recommended by the manufacturer (1000 ppm).
For testing we used a motor stand with gasoline 16-valves a fuel injected
engine VAZ-2112 (4H 8.2/7.1) capacity 68 kW at rpm
n
= 5600 rpm.
Test procedure each sample of gasoline included the following stages
[9, 10]:
•
partial disassembly of the engine, weighing the weight of the control
elements (valves, spark plugs, injectors), Assembly, installation stand;
•
reference contamination — development on a fixed mode, 20 litres
special dirt mixture forming on the surfaces of the combustion chamber,
the fuel and intake systems of the engine starting of the deposition layer;
•
repeated partial disassembly, the determination of the initial mass of
sediments Assembly;
•
the initial lifting of the performance of the engine for a given pro-
gram with the measurement of instantaneous fuel consumption and toxici-
ty of exhaust gases on the load characteristics in the operational range of
the engine. It is not allowed to work the engine at high loads to exclude
the factor self-cleaning temperature of the engine;
•
holding a twenty-hour test cycle for variable modes of the subject
gasoline;